Treatments to Relieve Ball of Foot Pain
- Home
- Treatments to Relieve Ball of Foot Pain


Our feet play a crucial role in facilitating movement and supporting our entire body. With every step, an intricate system is at work to keep us mobile and balanced. Oftentimes, we don’t realise how crucial the foot is to our well-being. From working out, strolling to the supermarket, and preparing meals, our feet enable us to perform daily duties with ease.
When your forefoot is subjected to too much stress, the ball of the foot may become inflamed. The ball of the foot is located in the cushioned part of your sole between the toes and the arch. In Singapore, ball of foot pain treatment is accessible for people of all ages.
(Image source: https://www.perthfootcentre.com.au/do-you-get-pain-under-the-ball-of-your-foot/)
The base of your foot is made up of long bones called metatarsalgia, which connect the toes to the ankles. Each foot contains five metatarsal bones — one for each of the toes, with the exception of the big toe (Dwyer, 2009). Ball of foot pain is commonly felt in the area under the metatarsal heads, which aid in balance and mobility. There are reasons why we should address ball of foot pain:
High-impact pressure on the foot is common after a taking part in sports such as football, baseball, and tennis. The main causes are bone related problems of the forefoot, which can be divided into hallux (big toe) and lesser toes.
The cause is almost always linked to imbalances in the foot alignment or muscles of the foot and lower leg. Hallux valgus is one of the most common causes for forefoot pain. It is a forefoot deformity caused by a combination of genetic susceptibility and the use of tight shoe wear and heels. Rarer causes of forefoot pain include problems with nerves and vessels of the foot (Cleveland Clinic, 2021).
The causes include deformities of the foot, injuries to the ankle and foot region and muscle & nerve related ailments. The source of pain in the forefoot includes pain from the bone, pain from ligaments and tendons, and pain from nerve problems. Symptoms can be felt below your toes and it can appear as:
People may develop symptoms quickly or over a long period of time. This condition, if left untreated, can spread to other areas of the body. The hip and lower back will need to compensate for the foot pain and abnormal walking pattern (Gotter, 2023).
Anyone can develop ball of foot pain. There are risk factors that make you susceptible to this condition, including intrinsic and extrinsic sources (Weatherford & Irwin):
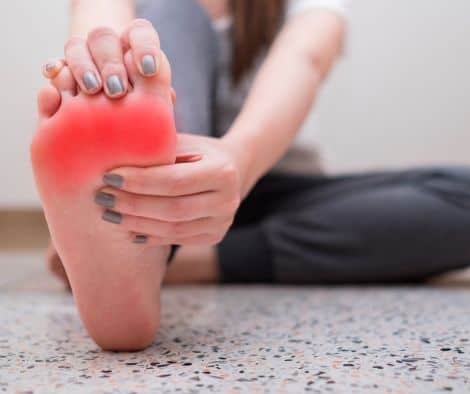
(image source: https://www.fairfieldpodiatry.com.au/blog/2021/8/3/ball-of-the-foot-pain-from-running)
After a long day on your feet or a particularly strenuous workout, your feet may start to hurt. If your ball of foot pain persists, you should see a doctor (Gotter, 2023). Discomfort after 2 to 3 weeks of the initial injury or start of the pain is a cause for alarm. You should contact an orthopaedic surgeon if you experience:
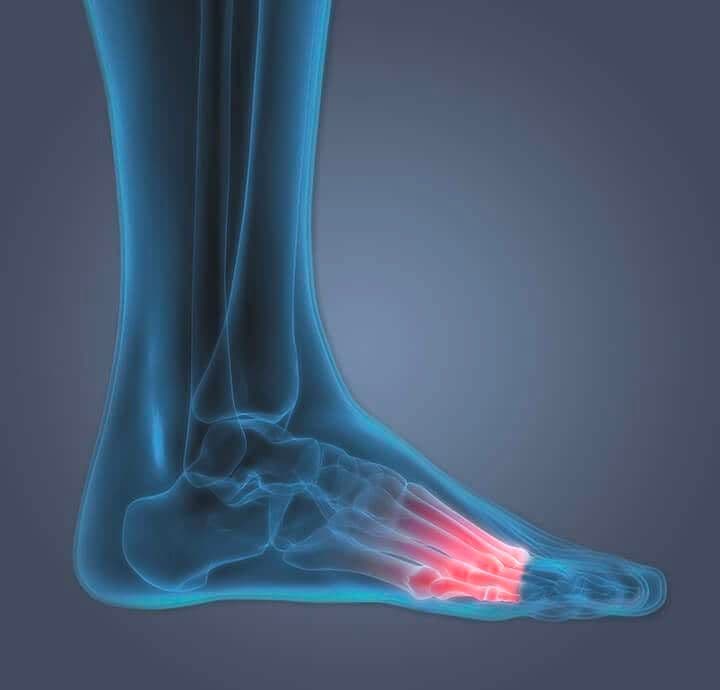
(image source:https://www.drscholls.com/ca/symptoms-and-conditions/foot-pain-and-conditions/
ball-of-foot-pain/#:~:text=Rest%3A%20By%20reducing%20stress%20on,20%20minutes%20at%20a%20time)
Your orthopaedic surgeon will first conduct a medical interview and clinical examination (Cleveland Clinic, 2021). You may also have to undergo MRI scans and specialised x-rays of the foot & ankle. Afterward, your doctor will recommend a treatment plan which can comprise of:

(image source: https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/woman-stretching/3)
General foot health can be improved by making lifestyle changes, such as switching to proper footwear, watching one’s weight, and engaging in regular stretching and strengthening activities. Athletes should also ensure that they undergo proper training techniques. It is also important to rest, elevate your leg, and use ice packs for acute causes of forefoot pain (Gotter, 2023).
Forefoot pain is usually a complex constellation of problems and imbalances in the foot. Focusing on one region of the foot may not be sufficient, and it is often necessary to correct imbalances elsewhere to achieve lasting relief. Oftentimes, we may forget to take care of our feet. If you experience foot pain, remember to take breaks, and contact your orthopaedic surgeon for ball of foot pain treatments if your symptoms do not subside.
– It is caused by hallux pain such as hallux valgus (big toe) or hallux rigidus (bunion), lesser toe pain such as transfer metatarsalgia or stress fractures, and nerve related conditions such as Morton’s neuroma.
– See “Identifying Causes of Ball of Foot Pain” for more information.
– If pain does not resolve within 2 to 3 weeks of the initial injury or start of the pain, you should seek help from your orthopaedic surgeon. Some patients experience severe pain that prevents them from walking or finishing daily activities. You should also medical assistance if the pain does not go away even after first aid, rest, or lifestyle modifications.
– See “Seeking Medical Help for Ball of Foot Pain” for additional details.
– Paracetamol and ibuprofen are common pain medications which can provide relief, but they are typically not effective for moderate to severe pain.
– See “Diagnosis and Treatments for Ball of Foot Pain” for a list of potential treatments.
– Vitamins and supplements may not be beneficial for this condition. Your orthopaedic surgeon will advise you on the best treatment plan for your unique needs.
– See “Diagnosis and Treatments for Ball of Foot Pain” for a list of potential treatments.
– Athletes do high-intensity activities during training. They can engage in effective warm-up and cool down exercises and use taping and good shoe wear to prevent traumatic causes of forefoot pain.
– See “Lifestyle Changes to Manage Ball of Foot Pain”for more tips.
– Depending on the cause of forefoot pain, acupuncture may have a limited role especially if the cause is muscular in nature. Some patients may prefer to utilise this method, but its relief tends to be short-lived.
– Proper rest, elevation, icing can be effective for acute causes of forefoot pain if performed immediately after injury. If symptoms persist or worsen, you should book an appointment with your orthopaedic surgeon.
– Inadvertent overdosage of over-the-counter medications can happen if pain control is sub-optimal and patients overdose to try and control the pain. Some over-the-counter medications also cause abdominal pains, chest pains, nausea, and headaches.
– High heels tend to exacerbate forefoot pain and may result in tight calf muscles which can worsen forefoot pain. You can use cushioned footwear to prevent any injury or strain from daily activities.
– Depending on the condition, appropriate shoe modifications can offload areas of the forefoot that experience excessive stress. Your orthopaedic surgeon will recommend a customised treatment plan for you.
– Forefoot pain may have different causes. The treatment plan for the most common cause of forefoot pain, hallux valgus (bunion pain), involves minimally invasive techniques for treatment of the condition. Forefoot pain is usually a complex area of problems and imbalances in the foot. Addressing only the region that is painful may not be sufficient, and it is often necessary to correct imbalances elsewhere to achieve lasting relief.
– Main adjunctive treatment is in the use of physiotherapy to stretch and strengthen tissues and muscles. The use of appropriate foot orthotics such as custom shoe inserts can effectively support the feet and alleviate pain.
– In general, the type and timing of surgery depends on the severity and clinical presentation of the condition in question. For the most common cause of forefoot pain, which is hallux valgus, surgery can be conducted at an earlier stage to prevent worsening of the condition. As the type of surgery depends on the severity, early intervention typically means that less invasive methods can be recommended for the patient.
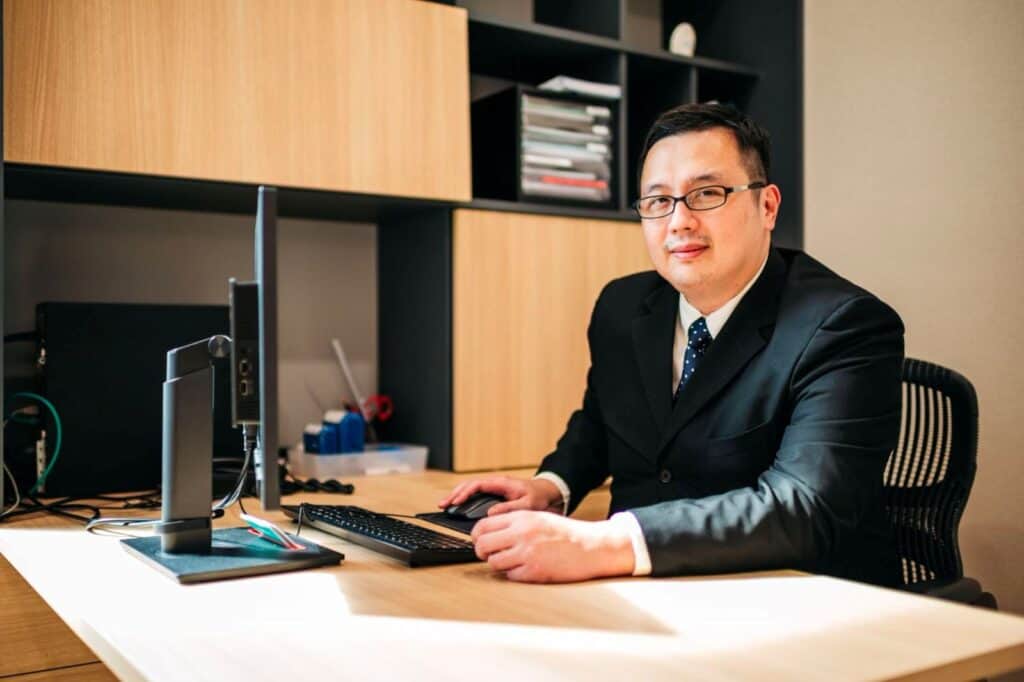

Dr Yong Ren graduated from the National University of Singapore’s Medical faculty and embarked on his orthopaedic career soon after. Upon completion of his training locally, he served briefly as an orthopaedic trauma surgeon in Khoo Teck Puat hospital before embarking on sub-specialty training in Switzerland at the famed Inselspital in Bern.
He underwent sub-specialty training in pelvic and spinal surgery, and upon his return to Singapore served as head of the orthopaedic trauma team till 2019. He continues to serve as Visiting Consultant to Khoo Teck Puat Hospital.
Well versed in a variety of orthopaedic surgeries, he also served as a member of the country council for the local branch of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen (Trauma) in Singapore. He was also involved in the training of many of the young doctors in Singapore and was appointed as an Assistant Professor by the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine. Prior to his entry into the private sector, he also served as core faculty for orthopaedic resident training by the National Healthcare Group.
Dr Yong Ren brings to the table his years of experience as a teacher and trainer in orthopaedic surgery. With his expertise in minimally invasive fracture surgery, pelvic reconstructive surgery, hip and knee surgery as well as spinal surgery, he is uniquely equipped with the tools and expertise necessary to help you on your road to recovery.
Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Metatarsalgia. Retrieved from
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15890-metatarsalgia
Dwyer, T. (2009). The Bone School. Retrieved from http://www.boneschool.com/
Gotter,A.(2023).Ball of Foot Pain. Retrieved from
https://www.healthline.com/health/ball-of-foot-pain
Weatherford, B. & Irwin, C. (2020). Footwear Guide. Retrieved
from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/staying-healthy/footwear-guide/